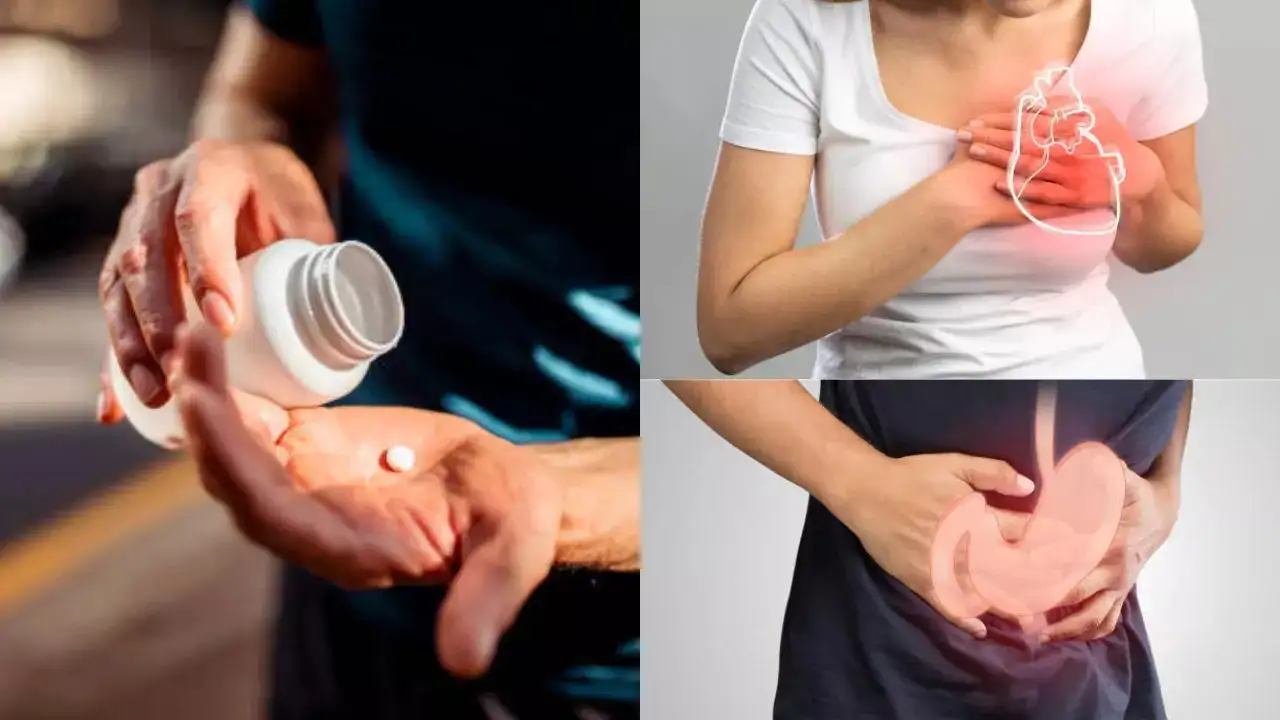
Dietary supplements sometimes not only interact with each other but can also be detrimental if you are taking other important medications as well
When it comes to daily supplements, there is always big hype about their potential benefits, which makes it hard to separate the facts from fiction. Even though experts vouch totally for vitamins and minerals as being essential to health, it is also true that taking them in pill, capsule, or powder form—especially in megadoses—can lead to dangerous consequences.
Dietary supplements sometimes not only interact with each other but can also be detrimental if you are taking other important medications as well. Unlike other drugs, supplements are not reviewed by any authority for safety and effectiveness before they are marketed. It’s up to manufacturers to ensure that their products do not contain contaminants or impurities, are properly labeled, and contain what they claim. In other words, there is no regulation, and so, it is important to know that you need to be careful while taking the doses.
But what happens when you overdose on supplements?
Doctors say overdosing on a few supplements can affect various aspects of your health, causing heart issues, kidney problems, and even liver failure.
Overdosing vitamin D can harm your kidneys
Vitamin D is among the most important nutrients that promote calcium absorption, and having enough is crucial for your overall health and well-being. It helps protect your bones and prevents arthritis, while also taking care of your mood and mental health.
However, experts say vitamin D should always be taken at the prescribed dosage, as higher amounts can lead to side effects ranging from muscle pain, mood disorders, abdominal pain, and gallstones to kidney failure and even heart attacks. It happens as vitamin D blood levels higher than 100 nanograms per milliliter can trigger extra calcium absorption in your body.
Also, vitamin D supplements and medications can interact with each other, as most drugs like statins, diuretics, and even weight loss medicines should not be taken together.
Excess calcium can settle in arteries
Calcium is important for a strong skeleton, but as with all nutrients, too much of this mineral may be harmful to your health. According to experts, more than 2,500 mg per day for adults ages 19-50 years and more than 2,000 mg per day for individuals 51 years and over can cause trouble.
Doctors say with calcium supplements, hardened arteries, or atherosclerosis, and a higher risk of heart disease are risks. You can easily get calcium from your diet by eating fruits, vegetables, and dairy products daily, as it gets better absorbed through food than through supplements.
The National Institutes of Health recommends 1,000 mg of calcium a day for women ages 19 to 50 and 1,200 mg a day for women 51 and older. The recommendation for men ages 19 to 70 is 1,000 mg a day and 1,200 mg a day for men 71 and older.
Kava overuse can harm your liver
Kava is an herb that helps treat general anxiety disorder in concentrated form. However, taking too much kava, or taking it for too long, has been linked to serious liver damage, including hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver failure.
As a result, the FDA has warned that people, especially those with liver disease or liver problems, or those who are taking drugs that can affect the liver, should talk to their healthcare practitioner before using Kava.
Many studies have also reported that heavy consumption of kava has been associated with heart problems and eye irritation. Several drugs may interact with Kava, from anticonvulsants to anti-anxiety medications and any drug metabolized by the liver.
Soy Isolates can create trouble with estrogen levels
While soy can be easily taken through tofu, tempeh, and soy milk, many people who take soy supplements need to be careful.
Many women take soy in supplement form because the plant contains estrogen-like compounds known as isoflavones that relieve symptoms of menopause. Yet some health experts have raised concerns that the isoflavones in soy supplements may contribute to an increased risk of breast cancer.
Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world.