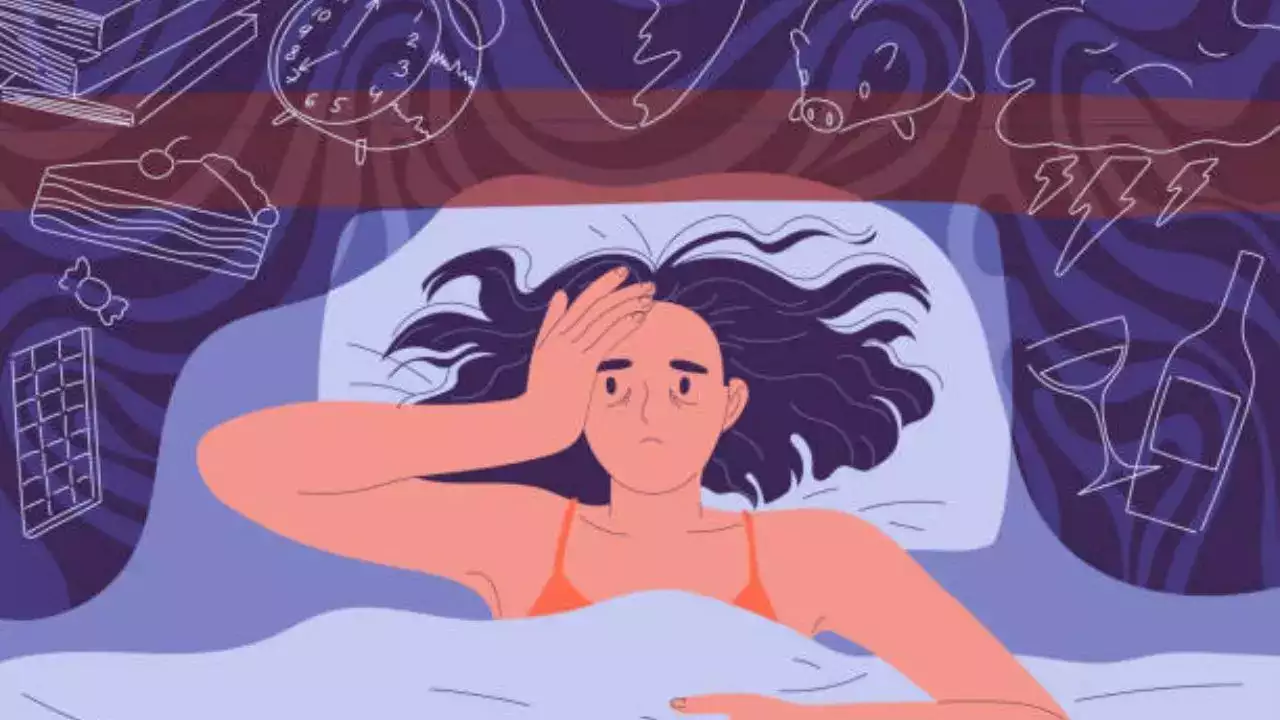
Anxiety spikes mostly at night when distractions from the day fade, leaving you alone with your thoughts
While you may feel exhausted after work by the time it is sunset, instead of taking a rest, most people scroll through their phones, answer messages, and replay the day’s events in their heads. All of this does not help you unwind but creates more anxiety.
According to experts, anxiety spikes mostly at night when distractions from the day fade, leaving you alone with your thoughts. A 2024 global survey found that 42 per cent of people struggle to sleep due to anxiety, while 27 per cent cite work-related stress.
Why does it happen?
The human brain cannot easily switch from high alert to deep sleep instantly. There are many habits, like thinking about work or eating too close to bedtime that can keep your nervous system in overdrive and make restful sleep feel impossible. Here are common habits that could be fueling your nighttime anxiety:
Doomscrolling
Whenever you choose to quickly scroll through your phone instead of resting at night, it can easily turn into an hour of consuming distressing news or endless reels and Instagram videos.
Experts say any kind of scrolling keeps your brain active and does not allow you to relax and get ready to sleep. This habit stimulates your brain’s stress response and induces the stress hormone, known as cortisol, which can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate your sleep cycle.
Taking medicines late at night
A few medicines, like antidepressants, decongestants, and even ADHD stimulants, are known to interfere with sleep or cause insomnia when taken in the later part of the day. Experts say these medications have similar effects as caffeine and can increase dopamine and norepinephrine, neurotransmitters that promote alertness and focus, and disrupt sleep.
Drinking coffee soda
When you drink coffee, soda, or tea at night, you may delay your body’s natural sleep process. According to experts, even when the effect gets worn off, you may have a hard time falling asleep. Caffeine blocks a sleep-inducing chemical known as adenosine, and it takes a while to exit your body.
Studies say caffeine has a six-hour half-life so if you drink 20 ounces at noon, there will still be around 10 ounces in your system by 6 p.m. and 5 ounces in your system at 12 a.m.
Eating heavy meals before bedtime
Eating heavy, greasy, or spicy meals before bed can lead to acid reflux, bloating, and fluctuations in blood sugar—all of which impact the quality of your sleep. Since your body prioritizes digestion, it will have a much harder time preparing for sleep.
However, eating too early may also affect your sleep.
How to reduce nighttime anxiety?
Doctors suggest you establish a comforting, anxiety-reducing routine, especially for your evening time, and make sure to follow it strictly, especially if you have an anxiety disorder.
Here are some tips to get you ready for a relaxing routine:
- Stick to a consistent bedtime so your body knows it’s time to unwind
- Avoid all screens two to three hours before bed
- Engage in relaxing activities like reading, stretching, or deep breathing exercises
- Dim the lights—no overhead lights—to encourage melatonin production
- Experiment with some wind-down techniques like journaling or meditation
Doctors say when your brain gets enough quality sleep, your impulse control will also improve, making it easier for you to shut down unwanted thoughts and regulate your emotions.
Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Mental Health, Health and around the world.