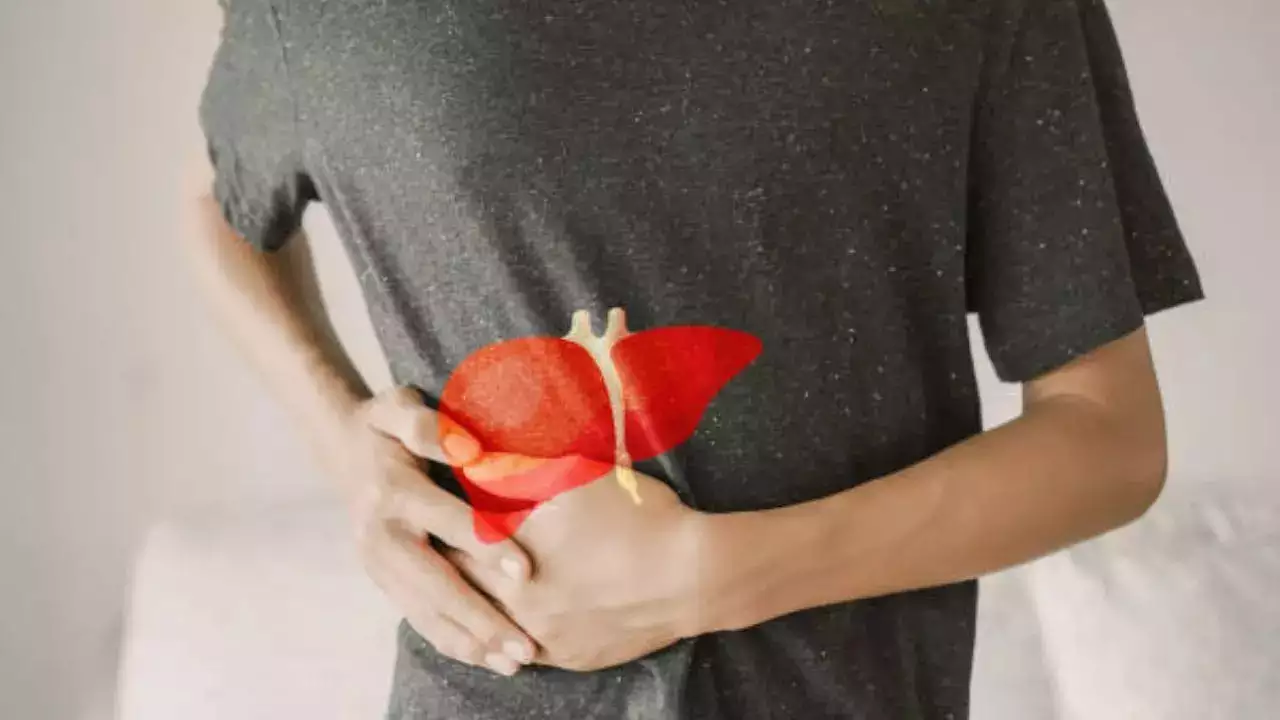
Silent Epidemic Alert! Fatty Liver Disease Rising Fast – Are You At Risk? (Image Credits: iStock)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), now recognized as Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD), is rapidly emerging as a major health concern in India. Experts warn that the country is facing a silent epidemic, with lifestyle factors contributing significantly to its rise. In response, the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) has released new guidelines to help manage and treat the condition effectively.
Diet and Exercise: Key To MAFLD Management
According to the APASL guidelines, diet and exercise play a crucial role in the management of MAFLD. The recommendations, published in the Hepatology International journal, explain that people with MAFLD who are also obese should aim to lose 5-10 per cent of their body weight. Experts suggest frequent self-weighing (at least once a week), adopting a reduced-calorie diet, and increasing physical activity for long-term weight management.
The guidelines show the benefits of combining diet with structured exercise. Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, reduces inflammation, and modifies metabolism in the liver, muscles, and fat tissues, thereby helping regulate free fatty acid flow to the liver.
Recommended Diet for MAFLD Patients
The APASL guidelines recommend a daily calorie intake of 1,200 to 1,800 kilocalories, or reducing 500-700 kilocalories per day, for effective MAFLD management. The Mediterranean diet is seen as the most evidence-based nutritional approach for addressing fatty liver disease.
This diet includes:
High intake of monounsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids
Although intermittent fasting has gained popularity for weight loss and metabolic benefits, the study authors caution that evidence regarding its effectiveness in reversing fatty liver disease remains limited. Interestingly, the guidelines suggest that consuming at least three cups of coffee daily may offer liver-protective benefits.
Exercise Guidelines for MAFLD Patients
To improve liver health and overall metabolism, the guidelines recommend engaging in 150-240 minutes of aerobic exercise per week. Even a minimum of 135 minutes weekly can provide substantial benefits. The suggested aerobic exercises include:
Running
Cycling
Swimming
Jumping rope
Symptoms of MAFLD
MAFLD often progresses silently, with many people remaining unaware of the condition until complications arise. However, common symptoms may include:
Unexplained weight loss
Pain or discomfort in the upper right abdomen
Swelling in the abdomen (ascites)
Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice in severe cases)
Preventive Measures
Since MAFLD is associated with lifestyle factors, preventive strategies are essential:
Maintain a healthy weight: Avoid obesity and engage in regular physical activity.
Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world.