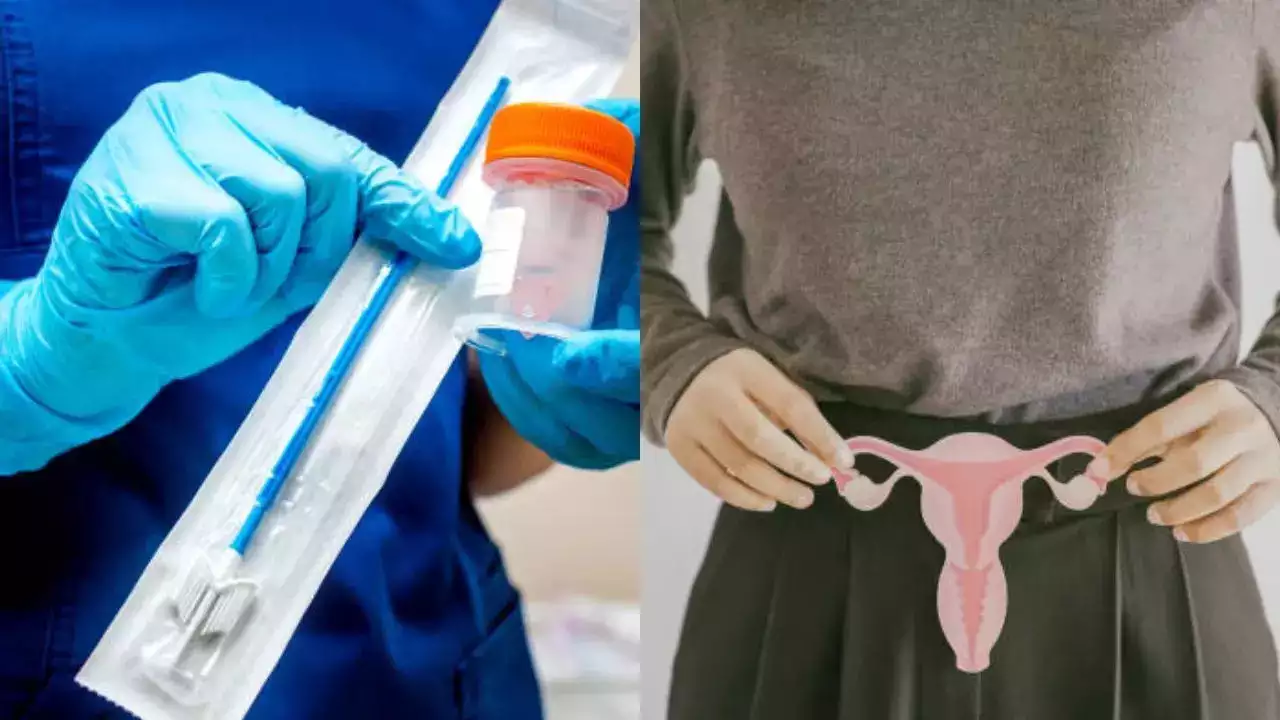
Gynaecologist Warns! Believing These 8 Myths About Cervical Cancer Are Delaying Timely Diagnosis (Image Credits: iStock)
Cervical cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women in India, and yet, misinformation about it is everywhere. The biggest culprit behind this rise? Human Papillomavirus (HPV). But there’s good news—as per experts cervical cancer is one of the most preventable cancers if detected early through screenings and vaccinations.
To help us get our facts right, we spoke with Dr Vaishali Paliwal, M.S, FMAS, M.Ch Gynaecological Oncology, MRCOG, Associate Consultant—Gynaecological Oncology, Max Saket Superspeciality Hospital, Delhi, who debunks the most common myths surrounding cervical cancer and HPV.
Myth 1: Cervical Cancer Is Rare
Fact: Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer among women in India. Dr Paliwal explains, “Many women present with the disease at an advanced stage, which drastically reduces the chances of a cure. However, it is highly preventable through regular screenings like Pap smears and HPV vaccinations.”
Myth 2: Only Older Women Are At Risk
Fact: Cervical cancer risk doesn’t increase with age. While it is most common in women between 35-45 years, there’s another rise in incidence between 55-65 years. “This bimodal age distribution is largely due to socio-cultural factors,” explains Dr Paliwal.
Myth 3: Cervical Cancer Always Has SymptomsFact: “Cervical cancer develops slowly and doesn’t always cause symptoms in the early stages,” says Dr Paliwal. That’s why regular screening is essential. A Pap smear and HPV DNA test can detect precancerous changes years before symptoms appear.
Myth 4: Pap Smears Are Painful And Invasive
Fact: Many women avoid Pap smears out of fear, but Dr Paliwal explains that: “The procedure takes less than 30 seconds. Yes, it involves a little discomfort as a small brush collects cells from the cervix, but it’s far less uncomfortable and painful than dealing with cervical cancer.”
Myth 5: Only People With Multiple Sexual Partners Get HPV
Fact: HPV is very common. “Anyone who is sexually active is at risk,” Dr Paliwal explains. Even using condoms doesn’t guarantee full protection, as HPV can spread through skin-to-skin contact.
Myth 6: HPV Infection Always Leads To Cervical CancerFact: Most HPV infections clear up on their own within two years. “Only about 10 per cent of cases result in persistent infections that could potentially lead to cervical cancer,” explains Dr Paliwal.
Myth 7: Cervical Cancer Is Hereditary And Contagious
Fact: Cervical cancer is not hereditary, but having a family history may increase your risk. It is also not contagious—you cannot “catch” cervical cancer from another person.
Myth 8: You Need A Pap Smear Every Year
Fact: “If your Pap smear and HPV test are normal, you only need to repeat them every 3-5 years,” says Dr Paliwal. However, women with a high risk of cervical cancer may need more frequent testing.
HPV is the leading cause of cervical cancer, but awareness, vaccination, and timely screening can prevent it. Dr Paliwal explains that “Vaccination against HPV is crucial for protection. Combine it with routine screenings, and we can significantly reduce cervical cancer cases.”
Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world.