Women are particularly significant as cases of oral cavity cancer are rising rapidly
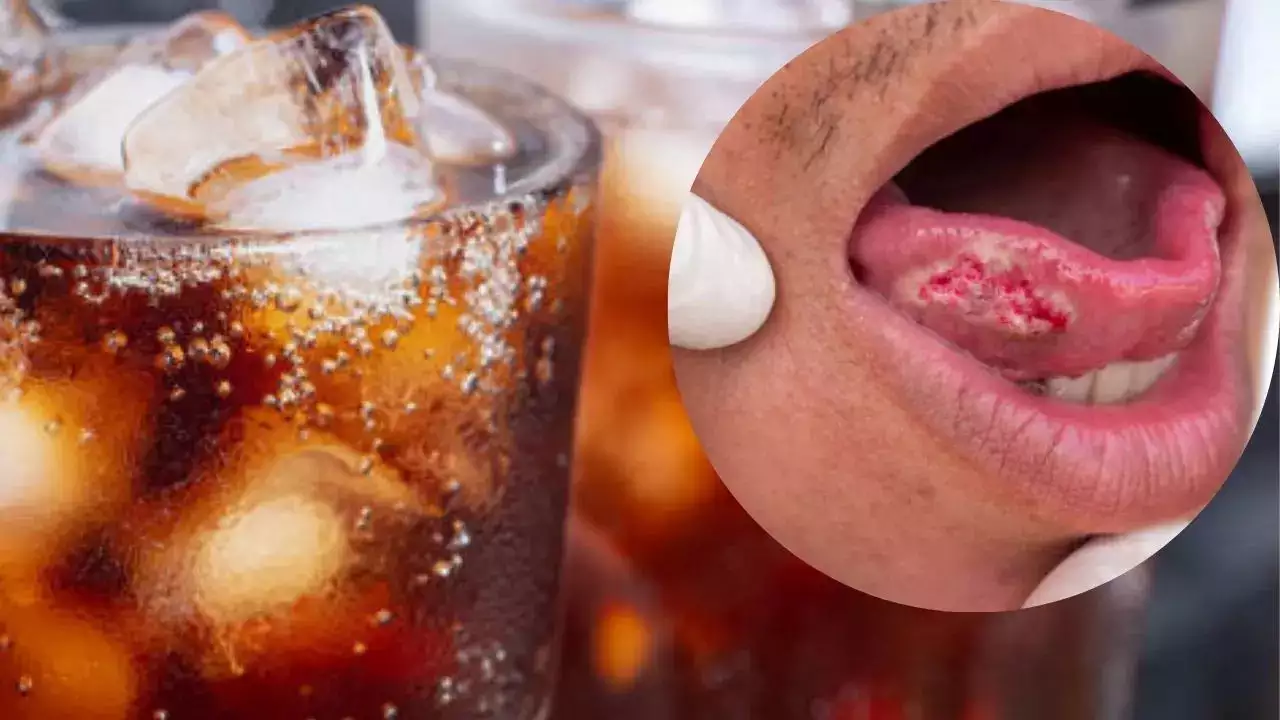
Women who consume at least one sugar-sweetened beverage daily have a five times higher chance of developing oral cancer, which forms in the oral cavity. Oral cancer forms when cells on the lips or in the mouth mutate in all parts of your mouth that you can see if you open wide and look in the mirror—lips, gums, tongue, cheeks, roof, or floor of the mouth.
A recent study conducted by the University of Washington discovered that women are particularly significant as cases of oral cavity cancer are rising rapidly, especially among younger people who do not smoke or drink and have no other clear risk factors.
Researchers suggest that diet might be playing a role in this alarming increase.
How do sweetened beverages cause cancer?
The study, published in JAMA Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, says while the beverages have been previously linked to colorectal and gastrointestinal cancers, their potential connection to head and neck cancers has not been explored until now.
"Oral cavity cancer is less common than breast or colon cancer, with an annual incidence of approximately 4-4.3 cases per 100,000. However, the incidence of oral cavity cancer is increasing in non-smoking, non-drinking women," Dr. Brittany Barber, the lead author of the study and assistant professor of otolaryngology head and neck surgery at the University of Washington School of Medicine, said.
While sugar itself may not cause cancer, excessive consumption leads to weight gain and obesity—significant risk factors for various cancers, including oral cancer. Also, experts believe that higher consumption of sugary drinks can cause a slew of other health effects, including inflammation and diabetes, which are also causes of cancer.
What is oral cancer?
Oral or mouth cancer affects the inside of your mouth ca may look like a common problem with your lips or in your mouth, like white patches or sores that bleed. The difference between a common problem and potential cancer is these changes do not go away. Left untreated, oral cancer spreads throughout your mouth and throat to other areas of your head and neck. According to experts, around 63 per cent of people with oral cavity cancer are alive five years after diagnosis.
Signs and symptoms of oral cancer
Oral cancer has several signs and symptoms that may be mistaken for common problems or changes in your mouth, which include:
-
Sores on your lip or inside your mouth that bleed easily and don’t heal within two weeks
- Rough spots or crusty areas on your lips, gums, or inside of your mouth
- Areas in your mouth that bleed for no obvious reason
- Numbness, pain, or tenderness on your face and neck or in your mouth that occur without apparent cause.
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing, speaking or moving your jaw or tongue
- Unintentional weight loss
- Earache
- Chronic bad breath
Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world.