Your muscles will become very weak, you could also feel dizzy, lightheaded, and even faint
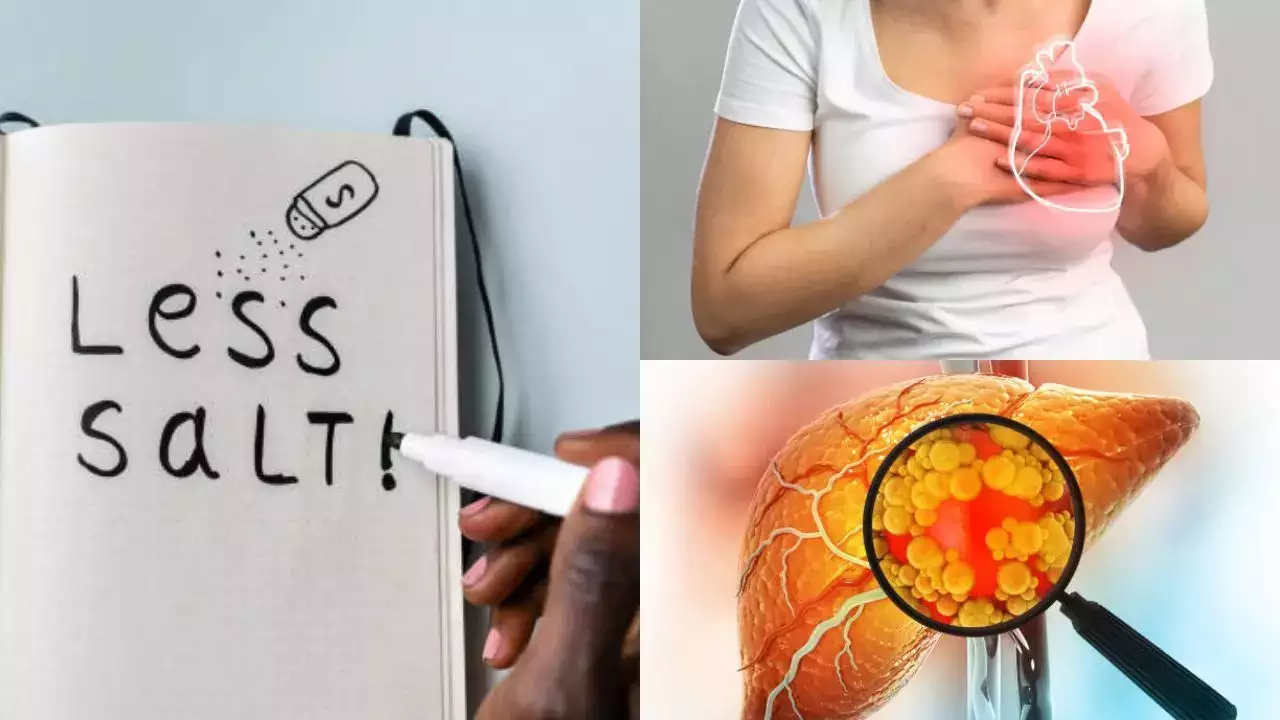
Eating too much salt can be dangerous for your health—especially your heart. A diet high in sodium increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and even kidney disease. However, eating too little can also be equally hazardous, according to a Harvard-educated doctor.
Dr Saurabh Sethi, a gastroenterologist, who regularly shares his experience and knowledge on social media, has warned of threats that come with eating salt less than a teaspoon a day. Dr Sethi explains that salt is a crucial electrolyte that helps your body retain water and hydrate it. “Without it, you would likely experience severe dehydration [and] your blood volume will decrease significantly, leading to a drop in blood pressure,” California-based Dr. Sethi said. He added that the craving for salty foods becomes “very intense."
And there are other dangers.
“Your muscles will become very weak; you could also feel dizzy, lightheaded, and even faint. On top of that, inadequate salt consumption can disrupt gut health by impairing digestion and weaken liver health by reducing essential nutrient absorption,” he added. “While many people worry about consuming too much salt, not getting enough can be far more dangerous."
What are the dangers of not eating salt?
Most current guidelines recommend eating less than 2,300 mg per day. And lower than that can lead to:
Increased risk of death from heart failure
Your heart may fail when it is not able to pump enough blood around the body to meet its needs for blood and oxygen. While this does not mean your heart stops working completely, it is still a very serious health issue.
According to Dr. Sethi, low-sodium diets are linked to an increased risk of death in people with heart failure.
Increases bad cholesterol levels
Not eating the required amount of salt can elevate the risk of heart disease, including increased LDL or bad cholesterol and triglyceride levels in your body. According to studies, low-sodium diets cause a nearly 5 per cent spike in LDL cholesterol and a 6 per cent high in triglycerides.
Increase in insulin resistance
Low-sodium diets are also linked to increased insulin resistance, which happens when your body’s cells do not respond well to signals from the hormone insulin, leading to higher insulin and blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance is a major driver of many serious diseases, including type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Causes dizziness, nausea
If you reduce the level of salt in your diet, it can lead to hyponatraemia, a condition when the level of sodium in your blood is lower than normal. It causes dizziness, nausea, and even fainting.
Weakens liver health
Those whose intake of salt in their daily diet is less are prone to liver issues, which can cause serious conditions like cirrhosis and ascites—fluid buildup in the abdomen. A low-sodium diet is recommended to help manage fluid retention and prevent complications.
Salt restriction can make food less palatable, leading to reduced appetite and caloric intake, which can worsen malnutrition, a common problem in liver disease.
Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world.